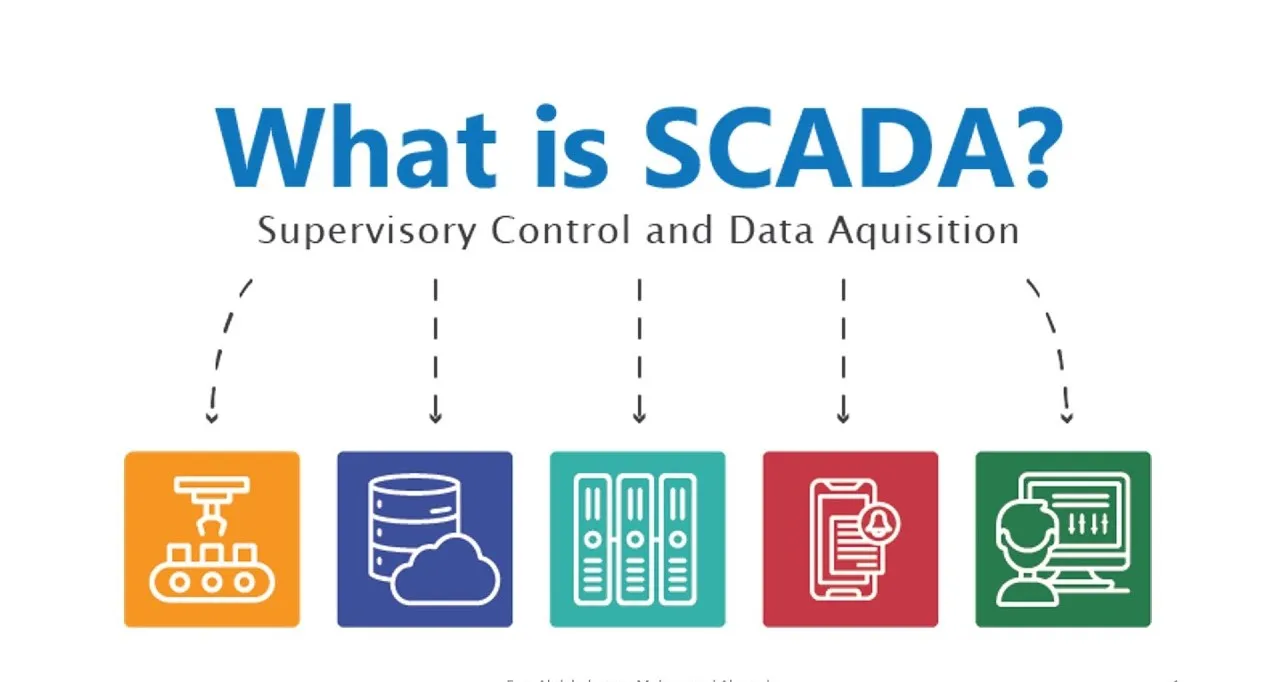
What is SCADA And How its Important For Industrial Automation?
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are the backbone of modern industrial operations. They provide the critical framework that allows organizations to monitor, manage, and optimize complex industrial processes from a central location. As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, understanding the role of SCADA industrial automation is essential for maintaining a competitive edge, boosting efficiency, and ensuring operational safety.
This guide will explain what SCADA is, how it works within an industrial automation context, and the benefits it offers across various sectors. We will explore its key components, its evolution, and what the future holds for this transformative technology.
By the end, you will have a clear understanding of why Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition is a cornerstone of modern industry and how it empowers businesses to achieve greater control and insight over their operations.
What is SCADA?
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. At its core, it is a system of software and hardware elements that allows industrial organizations to control processes locally or at remote locations. It also enables them to monitor, gather, and process real-time data.
Think of it as the central nervous system for an industrial plant. It gathers information from various sensors and instruments, presents it to human operators through a user-friendly interface, and allows those operators to control the processes.
For example, a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition system can alert an operator that a water tank is close to overflowing and allow them to remotely open a valve to release pressure. This combination of monitoring and control makes SCADA industrial automation a powerful tool for managing large-scale, complex systems.
Key Components of a SCADA System
A SCADA network is composed of several integrated components that work together to provide comprehensive control and monitoring. Understanding these parts is key to appreciating how the system functions.
Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
The Human-Machine Interface is the graphical user interface that allows an operator to interact with the Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition system. It presents operational data in a clear, visual format, often through diagrams, charts, and alarm notifications. The HMI is where operators can view system status, acknowledge alarms, and send control commands to the machinery. A well-designed HMI is intuitive, making it easier for personnel to manage complex processes effectively and respond quickly to issues.
Supervisory System
The supervisory system, or Master Terminal Unit (MTU), is the central hub of the Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition network. It consists of computers that communicate with all other components of the system. This central system is responsible for gathering data from the field devices and sending control commands to them. It houses the SCADA software and the processing power needed to analyze data, log events, and manage the overall operation.
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
Remote Terminal Units are microprocessor-controlled electronic devices deployed in the field at remote sites. They connect directly to sensors and actuators and are responsible for collecting data (like temperature, pressure, or flow rate) and translating it into a digital format that the supervisory system can understand. RTUs can also execute control commands sent from the master system, such as opening a valve or starting a motor.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
Similar to RTUs, Programmable Logic Controllers are often used as field devices within a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition system. While RTUs are better suited for widespread geographical telemetry, PLCs are typically used for more localized and complex control tasks, such as in a manufacturing plant. They are more flexible and can be programmed for a wider range of automation functions. In many modern SCADA industrial automation systems, PLCs and RTUs are used interchangeably or in combination to achieve the desired level of control.
Communication Infrastructure
The communication infrastructure is the network that connects the supervisory system with the RTUs and PLCs. This can include a mix of wired connections (like Ethernet and fiber optics) and wireless technologies (such as radio, cellular, or satellite). The reliability and speed of this network are critical, as it ensures that real-time data is transmitted accurately and control commands are delivered without delay.
The Role of SCADA in Industrial Automation
SCADA systems are fundamental to industrial automation, providing a centralized platform to manage distributed processes efficiently.
Real-Time Monitoring and Control
The primary function of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition is to provide real-time visibility and control over industrial processes. Operators can monitor equipment performance, track production metrics, and make immediate adjustments from a central control room. This capability is vital in industries where precise control is necessary to maintain product quality, ensure safety, and optimize resource usage. For example, in a power grid, SCADA allows operators to monitor electricity flow and reroute power to prevent outages.
Data Collection and Analysis
SCADA systems are powerful data-gathering tools. They collect vast amounts of historical and real-time data from every part of the industrial process. This data can be stored, trended, and analyzed to identify inefficiencies, predict maintenance needs, and optimize operations. By analyzing historical performance, businesses can make informed decisions to improve productivity and reduce operational costs.
Alarm and Event Management
An essential feature of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition industrial automation is its ability to manage alarms. The system is programmed with predefined setpoints for various operational parameters. If a parameter exceeds or falls below its setpoint (e.g., a tank level is too high or a temperature is too low), the SCADA system generates an alarm to alert the operator. This allows for prompt intervention, preventing equipment damage, production losses, and potential safety hazards.
Benefits Across Different Industries
SCADA systems are versatile and offer significant advantages to a wide range of sectors.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, SCADA helps manage production lines, monitor machine performance, and ensure product quality. It automates repetitive tasks, leading to increased output and reduced human error.
- Energy and Utilities: Power plants, water treatment facilities, and oil and gas pipelines rely heavily on SCADA to monitor and control vast, geographically dispersed infrastructure. It ensures a reliable supply and helps manage resources efficiently.
- Transportation: SCADA is used in railway systems to control signals, track trains, and manage power systems. It is also used in traffic control systems to optimize vehicle flow and enhance public safety.
- Building Management: In large commercial buildings and facilities, SCADA systems control HVAC, lighting, and security systems. This leads to improved energy efficiency and a more comfortable environment for occupants.
The Future is Integrated
The evolution of SCADA industrial automation is moving towards greater integration and intelligence. The rise of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is enabling more devices to be connected, generating even richer data sets. Modern Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition systems are increasingly cloud-based, offering greater scalability, accessibility, and data processing power. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is making SCADA systems more predictive and autonomous, capable of optimizing processes with minimal human intervention.
By adopting these advanced technologies, organizations can not only streamline their current operations but also prepare for the future of industrial automation. A robust and modern SCADA system provides the foundation for building a smarter, more efficient, and more resilient enterprise.